Kafka REST Porxy
The Kafka REST Proxy provides a RESTful interface to a Kafka cluster. It makes it easy to produce and consume data, view the state of the cluster, and perform administrative actions without using the native Kafka protocol or clients. Examples of use cases include reporting data to Kafka from any front-end app built in any language, ingesting data into a stream processing framework that doesn't yet support Kafka, and scripting administrative actions.
Some example use cases are:
- Reporting data to Kafka from any frontend app (Android and IOS) built in any language not supported by official Confluent clients
- In gesting messages into a stream processing framework that doesn’t yet support Kafka
- Scripting administrative actions
There is a plugin available for REST Proxy that helps authenticate incoming requests and propagates the authenticated principal to requests to Kafka. This enables REST Proxy clients to utilize the multi-tenant security features of the Kafka broker. For more information, see REST Proxy Security and REST Proxy Security Plugins.
API availability
The v3 API is the latest version of the API. The cluster ID is a path parameter to enable a REST Proxy to work with multiple Kafka clusters. API responses often contain links to related resources, such as the list of a topic's partitions. The content type is always application/json. Here are two examples to show how API used.
Get the local cluster information
$ curl http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters
Response:
{"kind":"KafkaClusterList",
"metadata":{"self":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters","next":null},
"data":[
{"kind":"KafkaCluster",
"metadata":{"self":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q",
"resource_name":"crn:///kafka=xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q"},
"cluster_id":"xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q",
"controller":{"related":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/brokers/0"},
"acls":{"related":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/acls"},
"brokers":{"related":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/brokers"},
"broker_configs":{"related":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/broker-configs"},
"consumer_groups":{"related":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/consumer-groups"},
"topics":{"related":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/topics"},
"partition_reassignments":{"related":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/topics/-/partitions/-/reassignment"}
}
]
}
Get a list of topics
$ curl http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/topics
Response:
{"kind":"KafkaTopicList",
"metadata":{"self":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/topics","next":null},
"data":[
{"kind":"KafkaTopic",
"metadata":{"self":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/topics/jsontest",
"resource_name":"crn:///kafka=xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/topic=jsontest"},
"cluster_id":"xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q",
"topic_name":"jsontest",
"is_internal":false,
"replication_factor":1,
"partitions_count":1,
"partitions":{"related":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/topics/jsontest/partitions"},
"configs":{"related":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/topics/jsontest/configs"},
"partition_reassignments":{"related":"http://localhost:8082/v3/clusters/xFhUvurESIeeCI87SXWR-Q/topics/jsontest/partitions/-/reassignment"}
}
]
}
Features
The following functionality is currently exposed and available through REST APIs.
-
Metadata - Most metadata about the cluster – brokers, topics, partitions, and configs – can be read using GET requests for the corresponding URLs.
-
Producers - Instead of exposing producer objects, the API accepts produce requests targeted at specific topics or partitions and routes them all through a small pool of producers.
-
Producer configuration - Producer instances are shared, so configs cannot be set on a per-request basis. However, you can adjust settings globally by passing new producer settings in the REST Proxy configuration. For example, you might pass in the compression.type option to enable site-wide compression to reduce storage and network overhead.
-
Consumers - Consumers are stateful and therefore tied to specific REST Proxy instances. Offset commit can be either automatic or explicitly requested by the user. Currently limited to one thread per consumer; use multiple consumers for higher throughput. The REST Proxy uses either the high level consumer (v1 api) or the new 0.9 consumer (v2 api) to implement consumer-groups that can read from topics.
-
Data Formats - The REST Proxy can read and write data using JSON, raw bytes encoded with base64 or using JSON-encoded Avro, Protobuf, or JSON Schema. With Avro, Protobuf, or JSON Schema, schemas are registered and validated against Schema Registry.
-
REST Proxy Clusters and Load Balancing - The REST Proxy is designed to support multiple instances running together to spread load and can safely be run behind various load balancing mechanisms (e.g. round robin DNS, discovery services, load balancers) as long as instances are configured correctly.
-
Simple Consumer - The high-level consumer should generally be preferred. However, it is occasionally useful to use low-level read operations, for example to retrieve messages at specific offsets.
-
Admin operations - With the API v3, you can create or delete topics, and update or reset topic configurations. For hands-on examples, see the Confluent Admin REST APIs demo. (To start the demo, clone the Confluent demo-scene repository from GitHub then follow the guide for the Confluent Admin REST APIs demo.)
Architecture and workflow
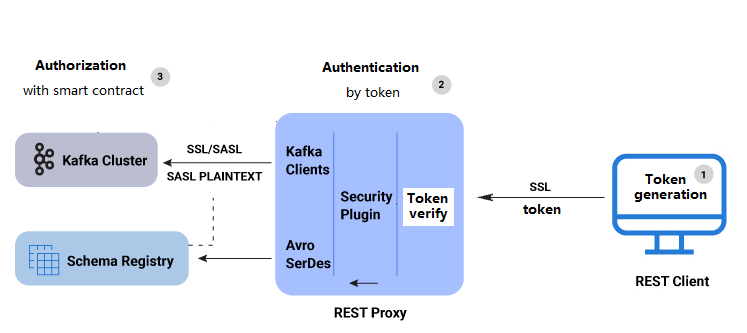
Here is a summary of the RBAC REST Proxy security workflow:
- A user makes REST API call to REST Proxy using LDAP credentials for HTTP Basic Authentication.
- REST Proxy authenticates the user with the MDS by acquiring a token for the authenticated user.
- The generated token is used to impersonate the user request and authenticate between Kafka clients and the Kafka cluster. For Kafka clients, the SASL_PLAINTEXT/SASL_SSL security protocol is used and the proprietary callback handler passes the token to the Kafka cluster. Similarly, when communicating with Schema Registry, the authentication token is passed to the Schema Registry client using a proprietary implementation of the BearerAuthCredentialProvider interface.
- If the user does not have the requisite role or ACL permission for the requested resource (for example, topic, group, or cluster), then the REST API call fails and returns an error with the HTTP 403 status code.